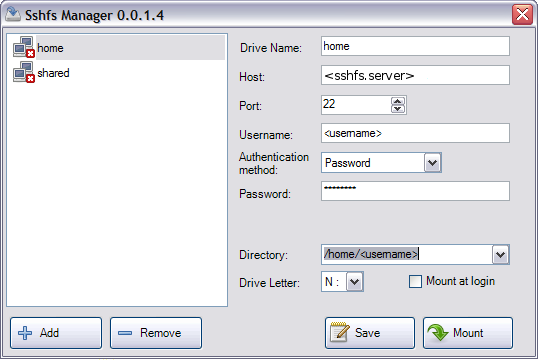
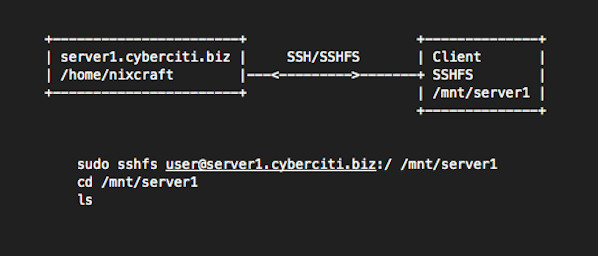
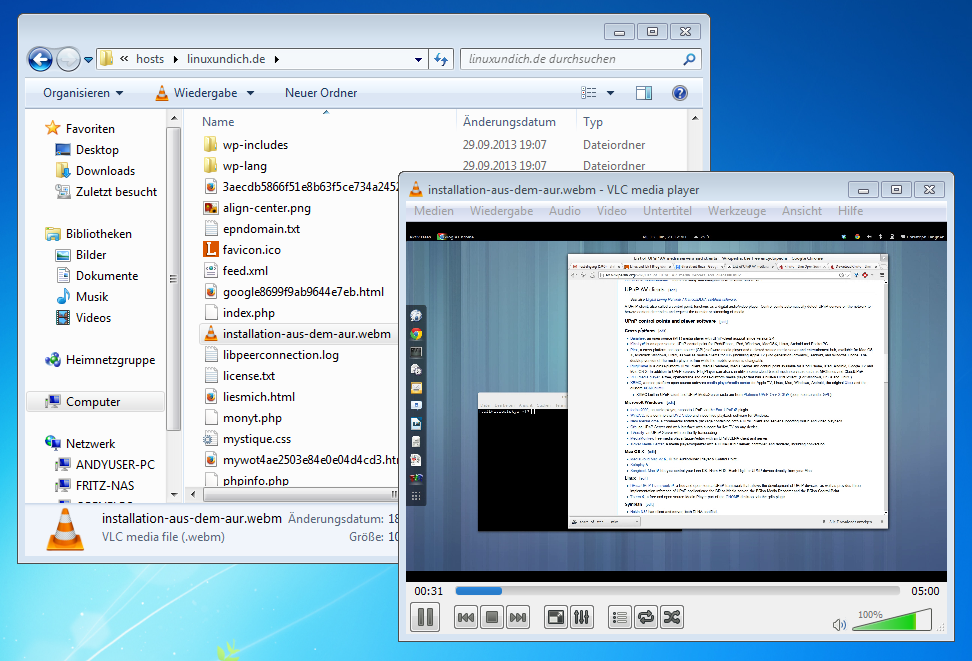
Connecting Host Open Fire Explorer and Map a Network Drive. Open a File Explorer. Right-click on This PC. Select Map network drive. Setup Share Drive. Once the wizard is opened, you will setup the share drive with the given information. Authenticate SSH Access. Microsoft announced it was bringing an integrated OpenSSH client to Windows in 2015. They've finally done it, and an SSH client is hidden in Windows 10's Fall Creators Update. You can now connect to an Secure Shell server from Windows without installing PuTTY or any other third-party software. Update: The built-in SSH client is now enabled by default in Windows 10's April 2018 Update. SSHFS for Shared Storage. HPC systems typically have some sort of shared filesystem (e.g., NFS, Lustre, BeeGFS), each with pros and cons. One solution often overlooked is sshfs, which belongs to a class of filesystems that work in userspace. For Linux, these filesystems are based on FUSE (Filesystems in Userspace) and have advantages and disadvantages, on which I won't elaborate here.
sshfs makes it convenient to mount a directory from a remote Linux computer on a local Linux computer. SSHFS-Win Cisco ise 2.4 ad integration. makes it easy to mount a directory from a remote Linux computer on your local Windows computer.
Install the latest stable installer of WinFSP from here.
Install the latest stable installer of SSHFS-Win from here.
Open File Explorer, right-click on This PC and choose Map network drive. Choose a drive to mount at and in the Folder field enter:
sshfsyourRemoteLogin@remoteComputer
By default, Windows will use your Windows password or credentials for the remote computer. If the password or credentials are different on the remote computer then choose the Connect using different credentials option.
Windows will ask for your password at the remote computer. After that the home directory from your remote computer will be mounted at the Windows drive you chose. I found that I had full read-write access to the files mounted from remote.
Sshfs Windows Subsystem For Linux
Tried with: SSHFS-Win 2.7.17334 and WinFSP 1.2.17346
Mounting an SSHFS network, the sign-on displays the desktop icon illustrated | |
| Developer(s) | Nikolaus Rath, Miklos Szeredi [1] |
|---|---|
| Stable release | |
| Repository | |
| Operating system | UNIX-like |
| Type | Remote access |
| Website | https://github.com/libfuse/sshfs |

Sshfs Windows To Linux
In computing, SSHFS (SSH Filesystem) is a filesystem client to mount and interact with directories and files located on a remote server or workstation over a normal ssh connection.[3] The client interacts with the remote file system via the SSH File Transfer Protocol (SFTP),[4] a network protocol providing file access, file transfer, and file management functionality over any reliable data stream that was designed as an extension of the Secure Shell protocol (SSH) version 2.0.
The current implementation of SSHFS using FUSE is a rewrite of an earlier version. The rewrite was done by Miklos Szeredi, who also wrote FUSE.[5]
Features[edit]
SFTP provides secure file transfer from a remote file system. While SFTP clients can transfer files and directories, they cannot mount the server's file system into the local directory tree. Using SSHFS, a remote file system may be treated in the same way as other volumes (such as hard drives or removable media).[6]
Using the Unix commandls with sshfs will sometimes not list the owner of a file correctly, although it is possible to map them manually.[7][8]
For distributed remote file systems with multiple users, protocols such as Apple Filing Protocol, Network File System and Server Message Block are more often used. SSHFS is an alternative to those protocols only in situations where users are confident that files and directories will not be targeted for writing by another user, at the same time.[citation needed]
Code filmora 7.8.9. The advantage of SSHFS when compared to other network file system protocols is that, given that a user already has SSH access to a host, it does not require any additional configuration work, or the opening of additional entry ports in a firewall.[5]
Windows Mount Sshfs
See also[edit]
- Files transferred over shell protocol (FISH)
- FileZilla, a free software utility for multiple platforms.
- SSH file transfer protocol (SFTP)
- Secure copy (SCP)
Sshfs Windows Root
References[edit]
- ^'SSHFS Contributors at Github.com'.
- ^ ab'Releases · libfuse/sshfs · GitHub'. GitHub. Retrieved 23 February 2020.
- ^'sysutils/sshfs-fuse: sshfs-fuse-2.4p1 – mount remote directories over ssh'. OpenBSD ports. 15 June 2013. Retrieved 10 February 2015.
- ^'SSHFS security'. Retrieved 26 February 2010.
- ^ ab'SSHFS homepage'. Retrieved 15 March 2012.
- ^'About SSHFS'.
- ^Canonical Ltd. (May 2009). 'SSHFS - Community Ubuntu Documentation'. Retrieved 5 June 2009.
- ^Szeredi, Miklos (November 2008). 'SSHFS FAQ: What options does sshfs support?'. Archived from the original on 18 April 2009. Retrieved 5 June 2009.
Sshfs Windows To Linux
In computing, SSHFS (SSH Filesystem) is a filesystem client to mount and interact with directories and files located on a remote server or workstation over a normal ssh connection.[3] The client interacts with the remote file system via the SSH File Transfer Protocol (SFTP),[4] a network protocol providing file access, file transfer, and file management functionality over any reliable data stream that was designed as an extension of the Secure Shell protocol (SSH) version 2.0.
The current implementation of SSHFS using FUSE is a rewrite of an earlier version. The rewrite was done by Miklos Szeredi, who also wrote FUSE.[5]
Features[edit]
SFTP provides secure file transfer from a remote file system. While SFTP clients can transfer files and directories, they cannot mount the server's file system into the local directory tree. Using SSHFS, a remote file system may be treated in the same way as other volumes (such as hard drives or removable media).[6]
Using the Unix commandls with sshfs will sometimes not list the owner of a file correctly, although it is possible to map them manually.[7][8]
For distributed remote file systems with multiple users, protocols such as Apple Filing Protocol, Network File System and Server Message Block are more often used. SSHFS is an alternative to those protocols only in situations where users are confident that files and directories will not be targeted for writing by another user, at the same time.[citation needed]
Code filmora 7.8.9. The advantage of SSHFS when compared to other network file system protocols is that, given that a user already has SSH access to a host, it does not require any additional configuration work, or the opening of additional entry ports in a firewall.[5]
Windows Mount Sshfs
See also[edit]
- Files transferred over shell protocol (FISH)
- FileZilla, a free software utility for multiple platforms.
- SSH file transfer protocol (SFTP)
- Secure copy (SCP)
Sshfs Windows Root
References[edit]
- ^'SSHFS Contributors at Github.com'.
- ^ ab'Releases · libfuse/sshfs · GitHub'. GitHub. Retrieved 23 February 2020.
- ^'sysutils/sshfs-fuse: sshfs-fuse-2.4p1 – mount remote directories over ssh'. OpenBSD ports. 15 June 2013. Retrieved 10 February 2015.
- ^'SSHFS security'. Retrieved 26 February 2010.
- ^ ab'SSHFS homepage'. Retrieved 15 March 2012.
- ^'About SSHFS'.
- ^Canonical Ltd. (May 2009). 'SSHFS - Community Ubuntu Documentation'. Retrieved 5 June 2009.
- ^Szeredi, Miklos (November 2008). 'SSHFS FAQ: What options does sshfs support?'. Archived from the original on 18 April 2009. Retrieved 5 June 2009.

